Liposomes are a form of lipid-based delivery that promote intestinal absorption, intracellular uptake and bio-availability of active nutrients
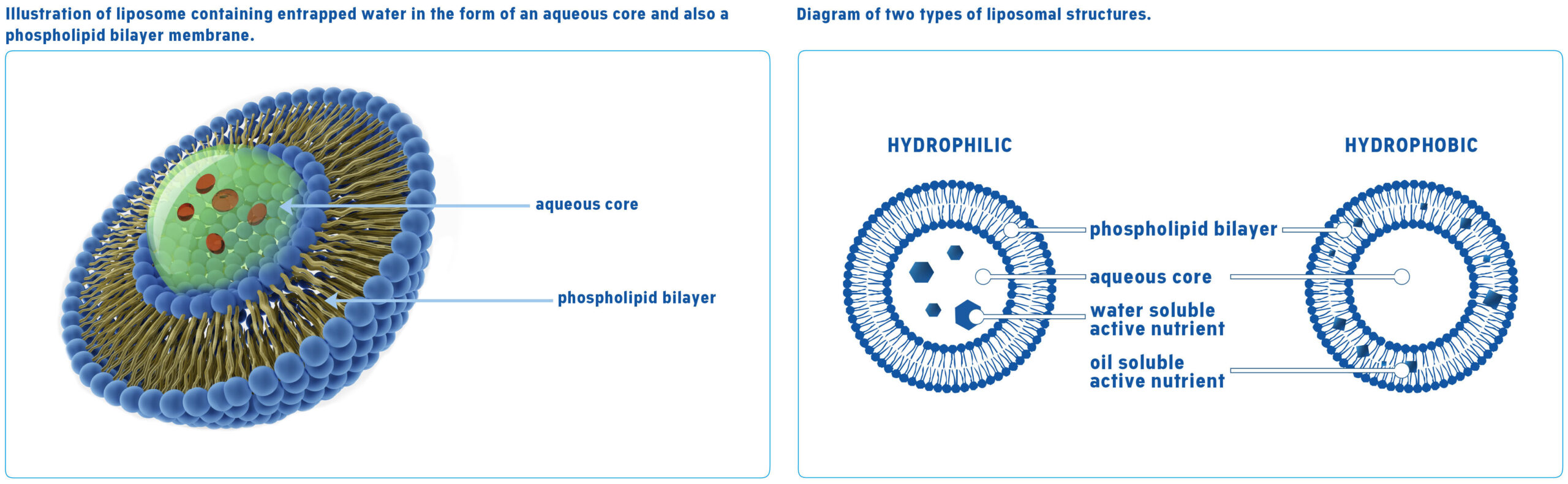
Liposomes are microscopic-sized spherical envelopes or pockets containing an aqueous core. The phospholipids are arranged into spherical cell membrane–like lipid bilayer, knows as a phospholipid bilayer. The centre of the liposome consists of an aqueous core.
Liposomes structures can be used for advanced delivery of key nutrients, which are then described as liposomal nutrients (e.g. liposomal iron).
Liposomal Delivery

Liposomes structures can be used for advanced delivery of key nutrients, which are then described as liposomal nutrients (e.g. liposomal iron). The liposomal nutrient is created through a careful manufacturing process resulting in an innovative delivery form of the nutrient with significant advantages for the consumer.
In the case of water-soluble nutrients (hydrophilic), the active nutrient is entrapped inside the aqueous core of the liposome. These liposome structures are found in liposomal vitamin C, iron, magnesium and glutathione.
Alternatively, in the case of hydrophobic (oil-soluble) nutrients, the active nutrient is enclosed within the phospholipids bilayer membrane of the liposome. These liposome structures are found in liposomal vitamin D and curcumin.
Lipsomal Delivery Manufacturing Process
The Liposomal nutrients used by Quest are supplied by Lipsovit® and manufactured using a carefully controlled manufacturing process. The liposome structures are additionally veri ed using cryogenic transmission and scanning electron microscopy.
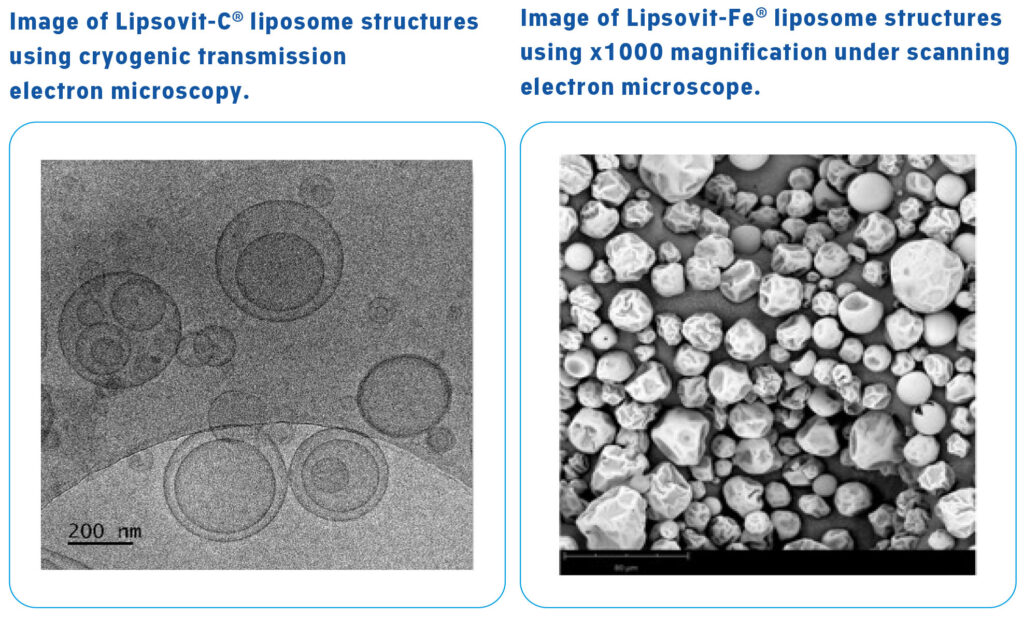
Particle size plays a vital role in nanoparticle adhesion to and interaction with biological cells in the body.1 2 At Quest we use Liposomal nutrients within a particle size of 200-400 nanometres (nm), ensuring they are a highly effective delivery system. The size of the liposomes and their particle size distribution are determined using a LUMiSizer® 651 particle size analyzer.

Advantages of Liposomal Delivery of Nutrients
The advantages of lipsomal nutrients are derived from the liposome structure itself. Liposomes contain both an aqueous core and a phospholipid membrane creating pockets of entrapped water along with water soluble active nutrients.
Active nutrients contained within the aqueous core are sealed within the protective phospholipid membrane. Lipsomal encapsulation provides a barrier around the active nutrient, increasing resistance to digestive enzymes, acidity, intestinal flora, and oxidation. This results in the protection of the active nutrient from degradation and oxidation as well as protecting the digestive tract from potential irritation by the nutrient, thereby improving delivery and bioavailability.
In addition, interactions between the liposome’s phospholipid bilayer membrane, containing hydrophobic active nutrients, and the body’s cell membranes offer enhanced cellular uptake through endosomal mechanisms.
As a result, the advantages of liposomal nutrients include:

Studies on Specific Liposomal Nutrients
Vitamin C Bioavailability
A study of vitamin C circulating blood plasma concentrations comparing oral administration of 4g liposomal vitamin C and 4g conventional vitamin C over four hours showed a +50% increase in absorption and bioavailability of liposomal vitamin C. Additional research has confirmed the magnitude of the advantages of liposomal vitamin C for bioavailability, including one study finding liposomal vitamin C was 1.77 times more bioavailable and another study showing liposomal vitamin C was 2.90-3.29 times more bioavailable than conventional vitamin C.
Vitamin D Faster Absorption
A study comparing the absorption and serum levels of individuals supplementing with 10,000iu of vitamin D3 in liposomal form versus conventional forms concluded that lipsomal vitamin D3 supplementation was twice as fast as conventional vitamin D3 supplementation in delivering Vitamin D3 to the body. The study showed that liposomal supplementation increased the serum levels within hours of supplementation, whereas the conventional supplementation had no e ect on serum levels in this time period. They concluded that the onset time required to elevate vitamin D3 levels in the body was significantly shorter for liposomal supplementation, concluding that liposomal delivery used faster absorption pathways due to the encapsulation of the vitamin D3 in liposome structures.
Iron Intracellular Delivery & Bioavailability
A study of intracellular iron transport at 50umol/L concentration for 120 minutes incubation period using a Caco-2 cell study found a >30% increase in cellular uptake of liposomal iron compared to iron glycinate. Two studies, including a randomized cross over trial, have showed that absorption and iron serum/plasma levels from liposomal iron supplementation was >50% higher than other iron forms.Another study comparing liposomal iron (30mg/day) to ferrous sulphate (105mg/day) supplementation for
12 weeks found that more patients taking liposomal iron achieved an increase in 2g of haemoglobin levels after the 12 week treatment.
Glutathione Intracellular Delivery
An in-vitro study investigating the replenishment of intracellular glutathione through oral supplementation found that liposomal glutathione was 100-times more potent compared to conventional glutathione administration. Another study found daily supplementation with 500mg of liposomal glutathione for two weeks signi cantly increased the body stores of glutathione ( increases >40%), increased immune function biomarkers (Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity increase >400%) and reduced oxidative stress markers (decrease >35%).
EU Regulatory Status of Liposomal Nutrients
The EU commission has determined that liposomal vitamin C is not novel in food and can be freely sold in the EU as it has been consumed to a significant degree by humans in the EU before 15 May 1997.
Liposomal nutrients are classi ed under the category of “soft nanomaterials” in the EU and subject to the EU Novel food regulations. However provided such liposomal nutrients have a particle size of more than 100nm, they fall outside the focus of the nanomaterial and EU novel food regulations. At Quest we use Liposomal nutrients within the 200-400nm range, ensuring they remain e ective as a delivery system.
Download Technical Paper
By entering your name and email address we may contact you by email or phone, subject to our privacy policy.

